So, you need to troubleshoot for those issues to resolve the BSOD error. There are a number of possible causes, with correspondingly different solutions. So, we recommend checking the Event Viewer or analyzing the minidump file to narrow them down before moving on to the actual solutions.
Causes for USER_MODE_HEALTH_MONITOR BSOD Error
Fixes for USER_MODE_HEALTH_MONITOR BSOD Error
First, you need to make sure your disk has enough free space. Lack of sufficient space affects the Kernel, leading it to not execute the necessary services or send periodic signals to monitor critical processes.
Hardware failure.Device driver issues.Outdated Operating System.Improper BIOS configuration.System file corruption.Malware infestation.
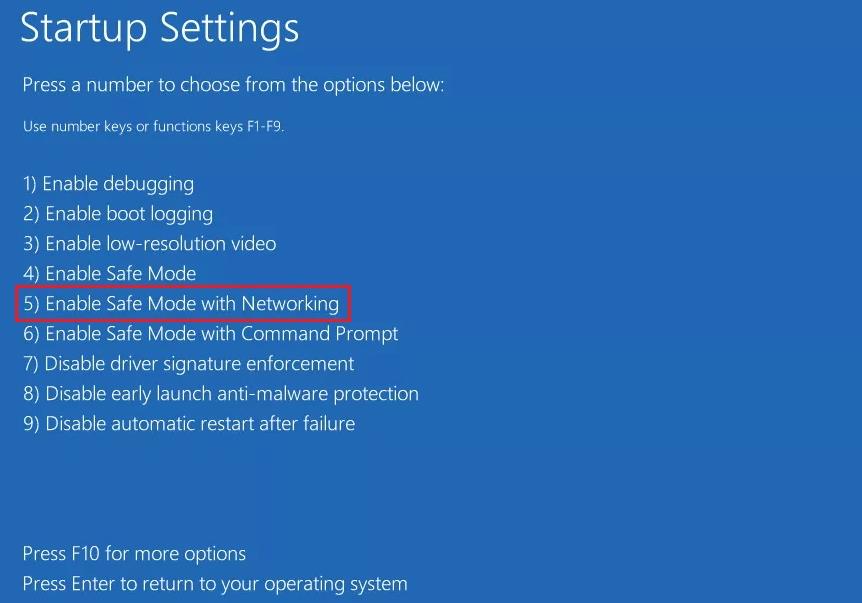
If you get stuck in a startup loop and can’t log in, you can try going to safe mode and free up space. Or you can connect your storage disk with another working system to perform this task. To boot in safe mode, You also need to boot in safe mode and perform the possible solutions we have mentioned below if you get stuck in a startup BSOD loop.
Remove External Devices
The first thing you should do if you encounter this issue is to remove external devices and restart your system. If the drivers of the devices or their hardware itself has some issues, they can fail the health check and cause this issue. If the computer runs without any issues after removing them, you need to update their drivers or reinstall them. First, you can analyze which device is responsible by connecting individual devices to the PC and checking whether the BSOD occurs. You should check the official websites for any incompatibility issues. If there are any conflicts, you may have to replace the device.
Run Startup Repair
If you get stuck in a BSOD loop, before moving on to further solutions, you should run Startup Repair. This program scans and repairs all the system files that are necessary for the start-up or boot process. So, if these files are causing the error, Startup Repair will be effective in resolving it. Here’s how you can do so:
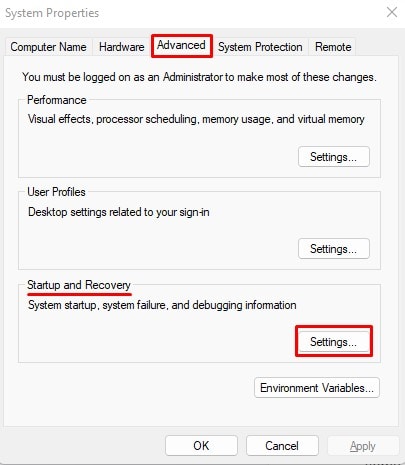
Disable Automatic Restart
If the BSOD crash starts occurring soon after you log in to your account, you won’t be able to perform all the troubleshooting steps. Windows also includes an option to disable automatic restart whenever the system encounters a BSOD bug-check. It is a protection feature that protects your software and hardware from damage due to improper system behavior. However, you can temporarily disable this option to allow yourself to debug the BSOD error. To do so, After resolving the issue, make sure to enable automatic restart again.
Check Event Viewer
You can check the Event log to determine the exact nature and cause of the BSOD crash. The event viewer keeps track of all the events your computer has encountered, so it’s an effective way to troubleshoot system issues. To check the application, We recommend checking out the Decoding Bugcheck 0x0000009E article on Microsoft Tech Community to understand these parameters. Then, you can search for the process ID on the internet to determine the process involved. You should also look through the events that occurred at the same time as the bugcheck to learn about other tasks your computer was running. They should also help you learn which component led to the BSOD.
Repair Corrupt System Files
Undesirable behavior of the system files may also lead to memory allocation and addressing issues, causing this error. Memory leaks, in particular, are very common due to issues with the file system. So, you should also check your system files for such corruption and repair them. The System File Checker (SFC) and Deployment Image Servicing and Management (DISM) are built-in Windows tools that you can use for such purposes. To run these tools,
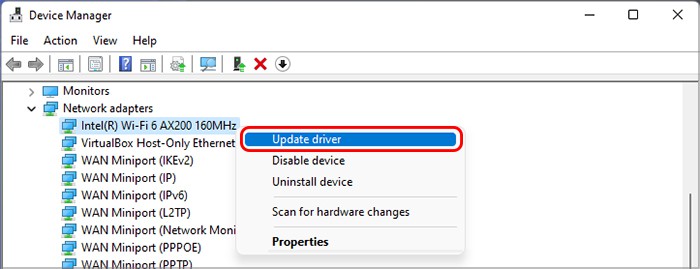
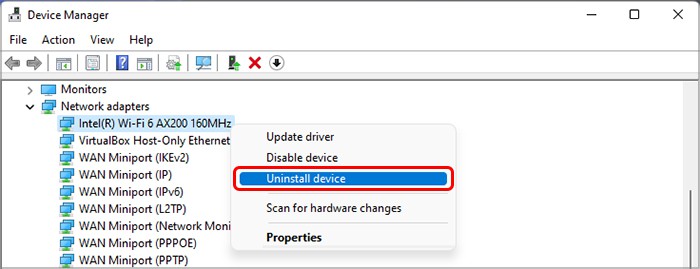
Update or Reinstall Drivers
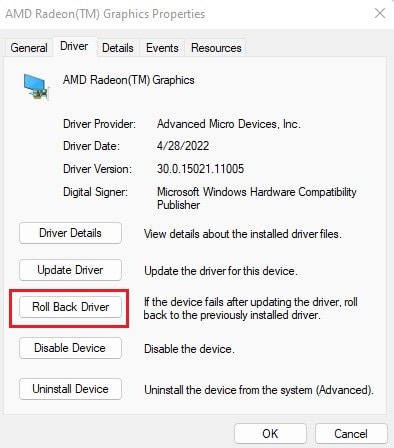
One of the main reasons for memory addressing issues or lock contentions is faulty drivers. We recommend updating all your drivers to prevent system issues. An outdated driver shows an exclamation mark next to its icon on the Device Manager so they are easy to look out for. If you install a new device to your system or were able to identify a driver as the reason for the BSOD, you definitely should update its drive. To do so, If you already have the latest version, you need to reinstall the driver. If it’s a Microsoft driver, simply uninstall it and restart your system. Windows installs all missing Microsoft drivers after a reboot. However, if it’s a third-party one, you need to uninstall it and then download and install the drivers from the official websites. Here’s how you can uninstall the driver: If you started encountering the issue after updating a certain driver, you can try rolling it back and check if the issue still occurs. To do so,
Troubleshoot Hardware Issues
This error also occurs whenever your hardware components fail. So you need to check for and troubleshoot all such issues.
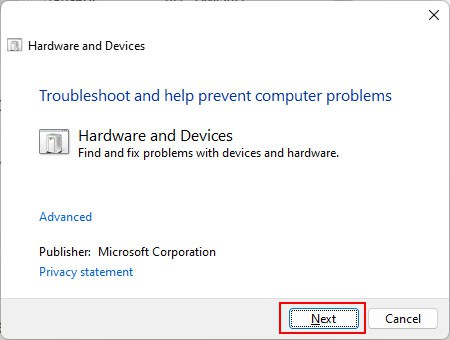
First, try using third-party monitoring software to check for any defects. If you find them, get help from a hardware expert for repair or replacement.You can also run the hardware and devices troubleshooter to check for any issues with your devices. To do so, enter msdt -id DeviceDiagnostic on Run and click Next.Then, you need to resolve the overheating issues. First, clean the inside of your computer, especially its fans and vents. If the coolers don’t dissipate enough heat, you should consider upgrading them.
Also, make sure to check for any connection issues on the hardware components.
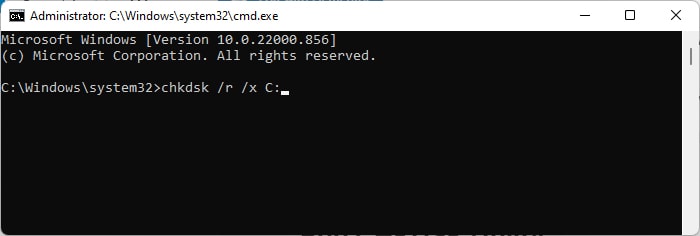
Repair Corrupted Disk
Windows includes the CHKDSK utility to scan and repair the corrupt disk sectors. So, you can use it whenever you encounter this error in case your disk has some issue. To run CHKDSK, If this utility fails to repair your disk, it is failing and you need a replacement.
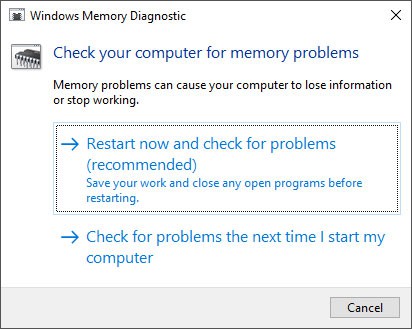
Run Windows Memory Diagnostic
Defective RAM is responsible for many kinds of BSOD errors, including this one. Windows contains a memory diagnostic troubleshooting app, which you can run to check for RAM defects. Here’s how you can do so, The memory diagnostic program starts running after a reboot. After the test finishes, your system restarts again and gives you the results. If you miss it, you can check on the event viewer. To do so, If the result shows there’s an error, your RAM stick or slot is defective. You can determine the faulty device by running the diagnostic app again while using separate RAM sticks on separate slots, one at a time. You need to replace the defective hardware to resolve the issue.
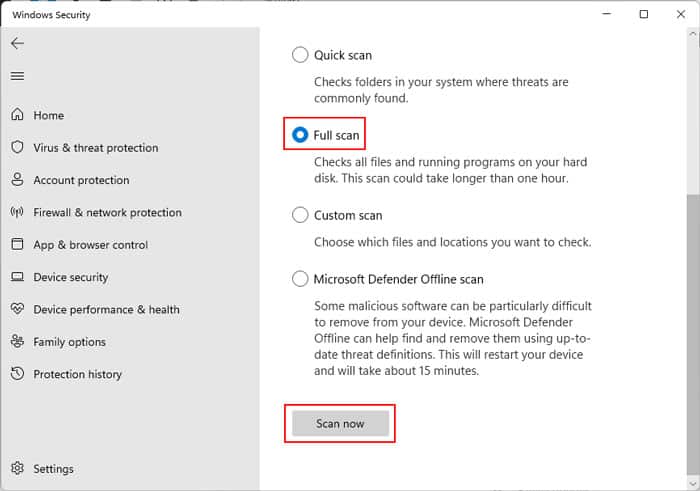
Scan for Malware
It is also possible that some malware scripts are infecting your drivers or other system files, causing critical services and programs to fail. Repairing the system files or other solutions we mentioned should resolve such issues. However, they don’t stop it from occurring again. For this, you need to scan your system with antivirus software. Here’s how you can do so using the Windows Security or Defender:
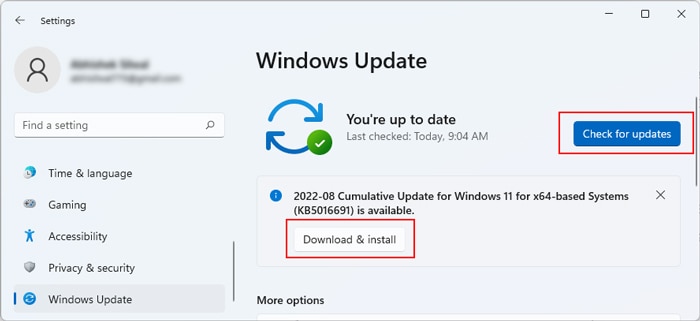
Update Windows
As we mentioned earlier, an incompatible device can cause this issue. However, Microsoft also releases compatibility patches on Windows updates, which resolve device conflicts. It is also possible that some system components are causing this issue due to a bug. Some versions of Windows OS contained bugs that caused failover cluster nodes to crash, resulting in this error. Microsoft has already released bug fixes for them, which you can find on its platform. You need to make sure you have the latest Windows version to prevent such issues. To update your system,
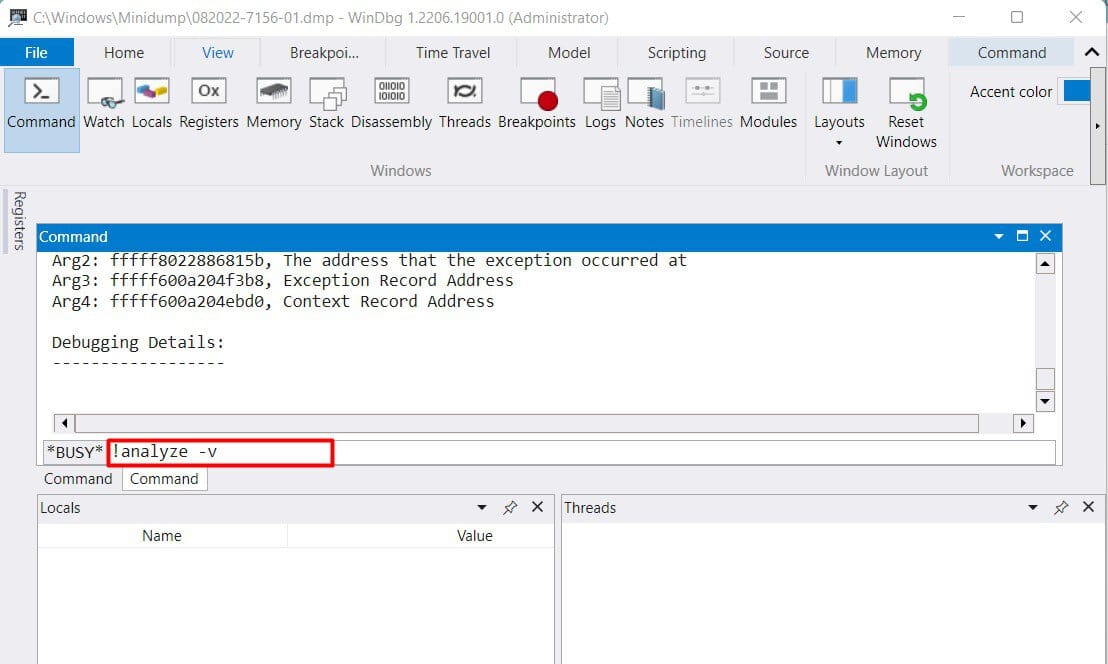
Analyze Minidump File
Analyzing minidump files is the best method you can use to isolate the cause for the issue. You can narrow it down to a particular software or driver. Here’s how you can analyze the minidump: If you have trouble determining the cause or analyzing the minidump, we recommend seeking help from Microsoft support forum.
Reset BIOS/UEFI
Improper configuration on the BIOS is also responsible for many hardware and memory issues. If you changed the setting to change your device configuration, such as for overclocking or enabling XMP, your system will start experiencing detrimental issues if your hardware can’t handle those configurations. In such cases, the easiest way to resolve the issue is by resetting the BIOS to the def. You can do so in the following ways:
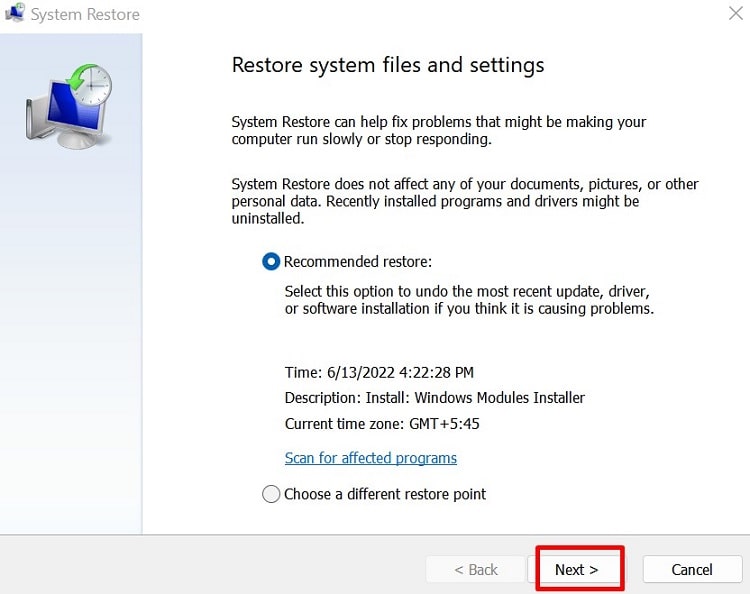
System Restore
If the previous methods were not helpful in resolving the issue, you need to restore your system to a previous restore point. This reverts your configuration, system files, and drivers back to the point, effectively resolving any errors you encountered afterward. Here’s how you can restore your system: If you don’t have a suitable restore point or the process doesn’t resolve the BSOD, you should reset your PC to the default state.