Cloning an MBR hard drive to GUID Partition Table (GPT) mode has other advantages as well. For example, you will boot into UEFI, instead of BIOS handling all the boot sequences, when using a GPT primary partition. UEFI handles this entire boot process and provides features such as improved boot performance and secure startup, that BIOS does not. Cloning MBR to MBR or GPT to GPT is a pretty straightforward, however, cloning MBR to GPT might not be as straightforward as you imagined. Worry not, for, in the article below, we explain exactly how you can accomplish this task.
Difference Between MBR and GPT
The basic difference between MBR and GPT lies in the fact that MBR primarily operates in legacy BIOS mode while GPT operates in EFI mode. The partition table in BIOS has a strict data structure that only allows four partitions. Thus, MBR can either have four primary partitions, or three primary partitions and one extended partition. UEFI can support 128 partitions by default. Also, BIOS is only able to address 32 bits at a time. Since a sector is 512 bytes in size, MBR can address a maximum of 2.19 TB of disk space. Whereas, EFI is able to address 64 bits and hence, GPT is compatible with up to 9.44 ZB disk space. When you boot your system, BIOS performs POST on your hardware then looks for bootloader in the MBR to load the OS. The bootloader in MBR is written into the first sector of the harddrive and is tied to the OS that is being loaded. You can have one bootloader in one primary partition. In contrast, when you are using a GPT mode, BIOS calls EFI scheme when booting. EFI handles everything and has a separate bootloader, called the UEFI bootloader. You can think of this as a mini operating system that is loaded directly into the memory before the UEFI executes additional instructions. Because of this, you can have different separate bootloaders for different OS when using UEFI mode.
How to Clone MBR to GPT
You might need to clone a MBR formatted hard drive (source) to a GPT formatted one (destination). First, you need to make sure that your destination disk is the same or larger size than your source drive. Thereafter, cloning MBR to GPT can be accomplished in three steps.
Convert GPT Destination Disk to MBR
The process of converting a GPT hard drive to MBR needs deletion of partition, and hence, loss of all data. Thus, it is advised that you backup all important files and documents before proceeding. You can accomplish this step using either of the two tools built into Windows, both of which are listed below. Pick one method that you like.
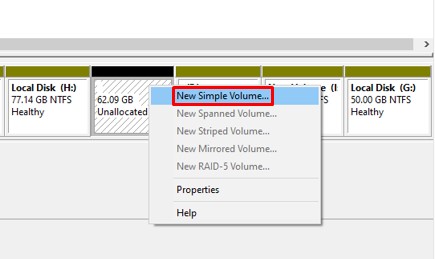
Convert to MBR Using Diskpart
Convert to MBR Using Disk Management Tool
Once your destination hard disk has been converted to MBR partition format, you can then clone your old hard drive onto the new disk using Clonezilla.
Cloning Hard Drive Using Clonezilla
You will need to install the destination hard drive (which you just changed from GPT to MBR), into the computer with the source MBR hard drive (which you need to clone). Thereafter, proceed with the steps below.
Convert MBR Back to GPT
After successfully cloning the hard drive, it is now time to convert the destination disk back to GPT format. We can utilize Microsoft’s built-in MBR2GPT.exe tool for this conversion. The conversion is done by applying the GPT components to MBR disk without modifying the existing partition or file systems. This process keeps your data intact. Make sure that your destination hard drive matches the prerequisites required for this command to run successfully. According to Microsoft, the required prerequisites are: After making sure that the required prerequisites are met, follow the steps below: Finally, if your destination disk had a larger partition size than your source drive, then you will find that the destination disk has lost some hard disk space. Don’t worry, the extra space is not lost, you can reclaim it. The destination drive now has been successfully cloned from the original MBR drive, and its partition format changed to GPT. If you have OS loaded onto this disk, it can now be used to boot into a UEFI enabled system.