A CPU temperature of 50-60 degrees Celsius at normal usage and 80-90 degrees during intensive work is quite common. But if the processor exceeds this temperature, then it is overheating. Unless your CPU is older or overclocked, overheating processor is usually the result of below-par heat dissipation. Whatever the cause, we are going to show how you can care for your CPU and prevent it from reaching higher temperatures.
Causes of an Overheating CPU
Fixes for Solving CPU Overheating Issue
At first, you need to be sure that your BIOS or the temperature monitoring application is showing the correct reading. You can use different software such as HWMonitor, Open Hardware Monitor, etc., to observe the temperature. See if all of them denote your CPU to be overheated.
Faulty CPU fan Accumulation of dust Inefficient air circulation Depleted thermal paste Low fan speed Overclocking the CPU Heavy programs running in the background Malware infection
If so, let’s move on to the fixes right away.
Find Processor-Hogging Programs
The CPU is designed to handle high loads most of the time. But some applications use a significantly high amount of processing power. When such programs run continuously in the background or foreground, it will cause the CPU to heat a lot. You can find such programs using Task manager and end them. Sometimes, the programs run in the background using the CPU silently. In such a case, you can disable background applications. Restart your system and see if it solved the issue. If the programs use high CPU again after the restart, then we recommend you uninstall them. You can also clean-boot your system to diagnose the exact process/application that’s causing the high CPU usage.
Look for malware
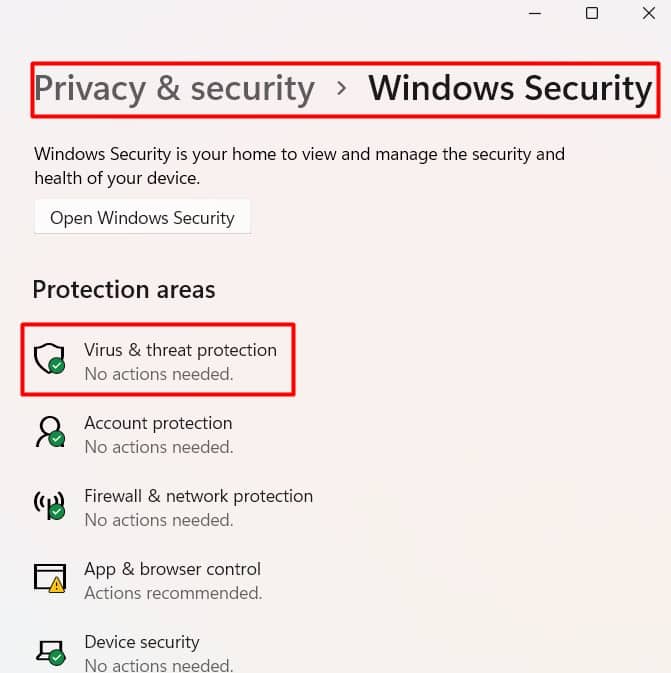
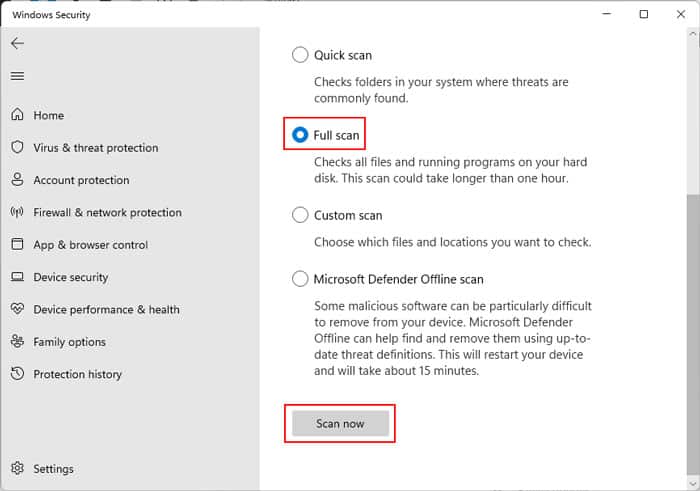
Not all CPU-hogging programs are intentional. If your system is infected with malware, they can use up the processor without any mercy. As a result, the CPU load increases, and it heats up more than its limit. You should run a complete virus scan on your system using the Windows defender tool. You could use a third-party antivirus, but it can consume additional processing power. Let’s run a virus scan using Defender. It can take a bit of time to complete the scan and remove the malware. See if the CPU temperature reduces after the virus scan.
Use a Dedicated Graphics Unit
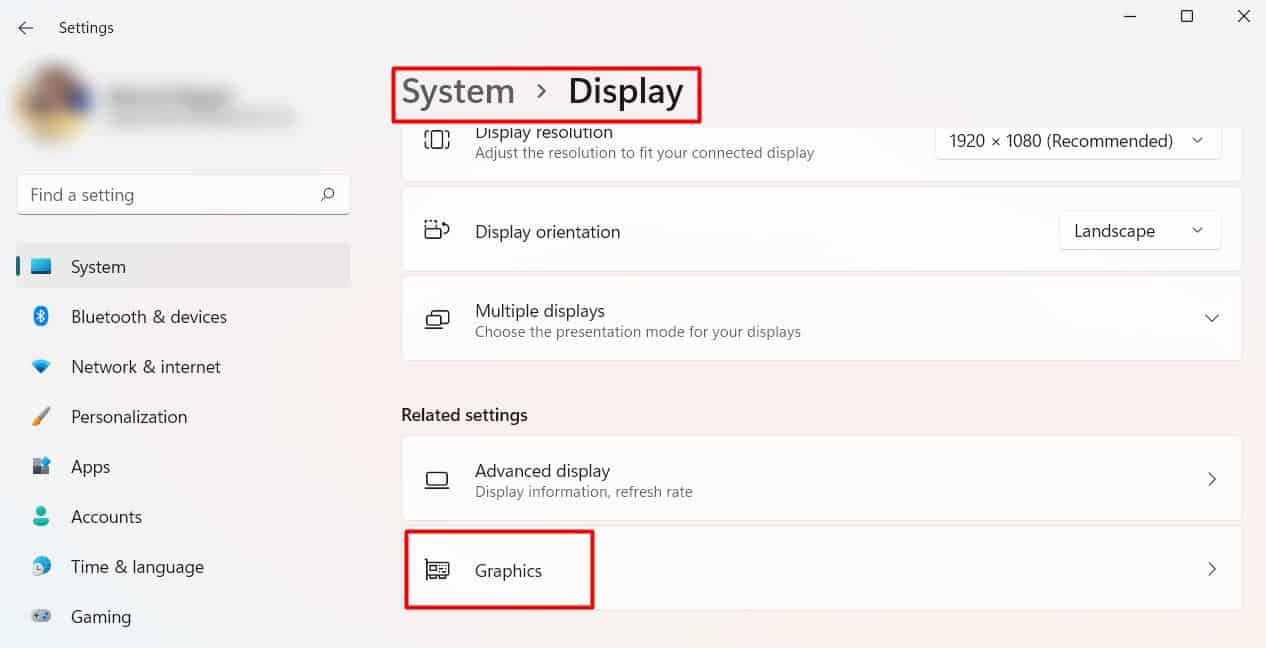
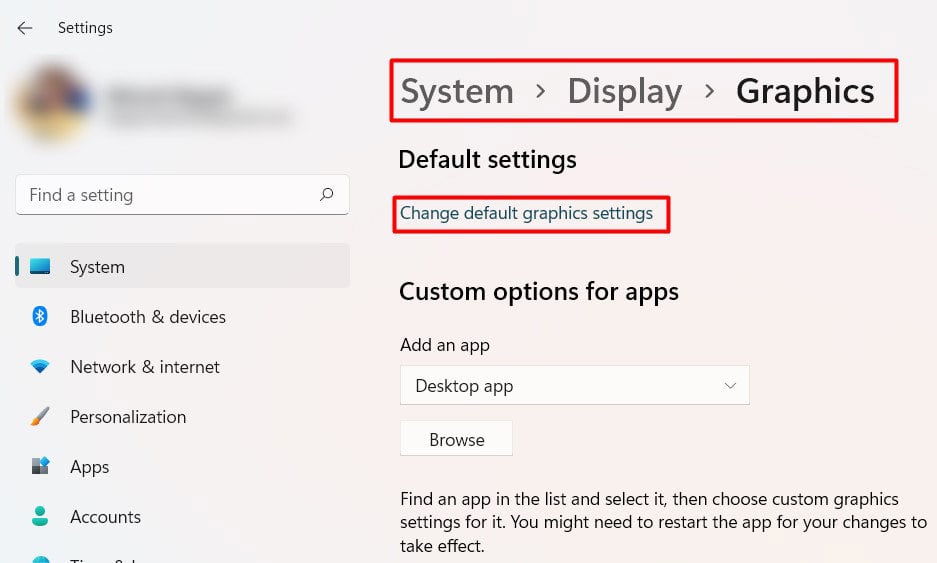
When you run a graphics-intensive program or simply a demanding application, it uses a lot of processing power. This can load the CPU even more if you run those applications using integrated graphics. The integrated graphics unit uses the CPU’s capacity to render the images. So, if you continuously use heavy programs and play high-end games, you should add a dedicated GPU to your system. The dedicated GPU has its own processor, memory, and cooling system. Using a GPU reduces the pressure on the CPU even more if you enable the Hardware Acceleration feature. This feature removes some load from the processor and uses other system resources such as GPU to run them. Let’s see how you can enable Hardware acceleration on your system. You should find your CPU temperature to decrease significantly.
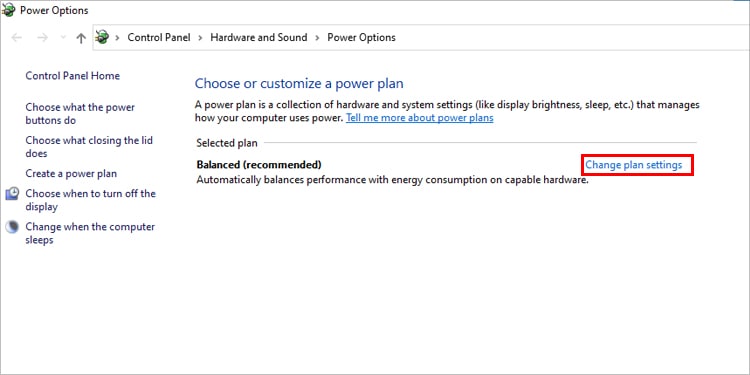
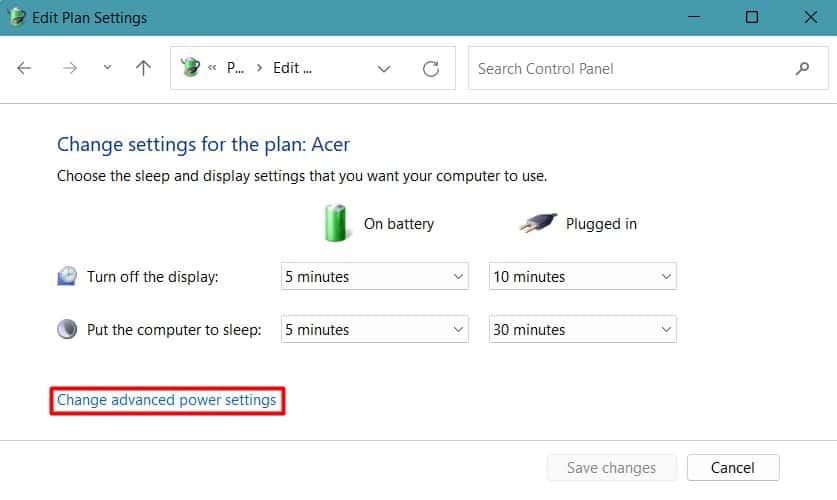
Reduce Maximum Processor State
Windows provide an option to manage the power plan and tweak the power usage settings of your system. If you are facing the CPU overheating problem in a laptop, you can use a balanced power plan or power-saving options. This provides a balanced performance and power usage compared to the High-performance setting. Similarly, you can also lower your Maximum processor state. If your processor is getting older and cannot handle higher loads, reducing the CPU usage percentage can help lower its temperature. Let’s see how you can set these settings on your PC. See if the CPU’s temperature comes to the normal range.
Stop overclocking
Most of us overclock our CPU to get the best performance out of it. It does the job excellently as well. But overclocking can increase the CPU temperature so much that it throttles to preserve its integrity. If you have overclocked your CPU, it may be a major reason for its high temperature. So, you should revert the overclocked settings to normal performance. Let’s see how you can do it. You can simply uninstall the program if you have used software to overclock your CPU. You should find your CPU running at normal clock speed and its temperature back to normal. In addition to overclocking, if you are active in cryptocurrency mining and use other heavy programs, they consume a lot of processing power. So, you can uninstall those programs to see any changes in the CPU temperature.
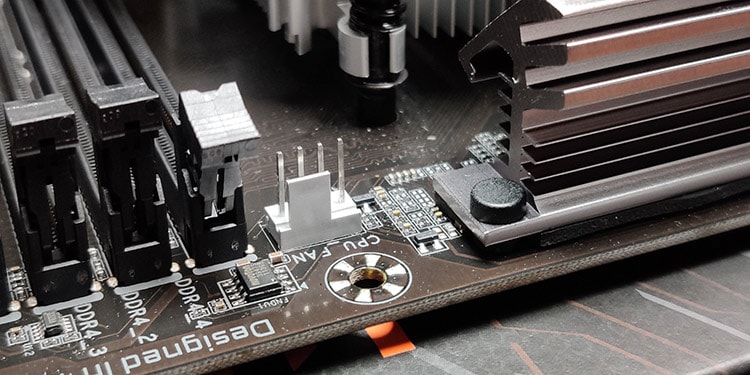
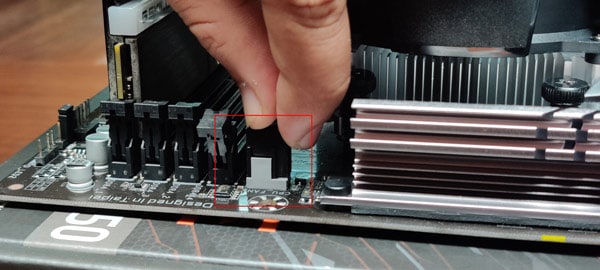
Check CPU Fan or AIO Pump
CPU fan is the major component responsible for maintaining the CPU temperature. If the fan is not working properly or is damaged, the CPU won’t get adequate cooling. So, you need to verify that the fan’s cable is not damaged or unplugged and its speed is sufficient for your system. Let’s disassemble your system to do it. Before re-assembling the system, let’s clean it first.
Clean the PC
Dust is the enemy which we can’t really avoid. Our system suffers from overheating issues when too much dust accumulates. It clogs the vents, slows down the fan, and insulates the heat sinks preventing them from dissipating heat. So, if you have not cleaned your PC in a while, the dirt collected on the CPU fan may have resulted in overheating of the CPU. While you are checking the fan, you need to clean your heatsink and the PC and free it from any dust. Operate your system and observe if the CPU temperature rises again.
Maintain Proper Airflow
The CPU fan draws the cold air inside and then pushes away the hot air to dissipate the heat generated in the CPU. But if the area is so congested that the fan cannot remove the air outside, the heat won’t get dissipated. As a result, the CPU overheats. This effect is more pronounced in laptops when you use them over a soft surface. The soft surfaces such as the mattress, compress and block the vents. Similarly, if the room air itself is hot or there is excessive sunlight falling on the system, then it will automatically heat up. So, you should use your system in a room or place with enough space for air circulation. Even better if the room has cooler airflow. Use the laptop on hard surfaces such as books or tables. It is more beneficial to get a laptop cooling pad.
Re-apply Thermal Paste
Thermal paste removes air bubbles between the CPU fan’s bottom and the processor to reduce insulation at the microscopic level. Thus, the heat gets transferred from the CPU to the heat sink much more effectively. But, over time, the thermal paste degrades, and the heat dissipation process may be ineffective, causing the CPU to overheat. Thus, you should remove the old thermal paste and re-apply the new one to the processor. Run the computer to see any changes in the CPU temperature.
Undervolt your CPU
When the processor’s load increases, it draws more power from the power supply unit. The high power draw increases the temperature in return. Undervolting a CPU means reducing its maximum working voltage by keeping its operating speed constant. So, when the voltage decreases, the temperature also reduces accordingly. Undervolting is one of the most used techniques to lower the CPU temperature. It is totally safe and, if done at an appropriate level, increases the performance even more. But there are several steps to follow while doing it. So, we have prepared a detailed guide on how to undervolt your CPU safely.
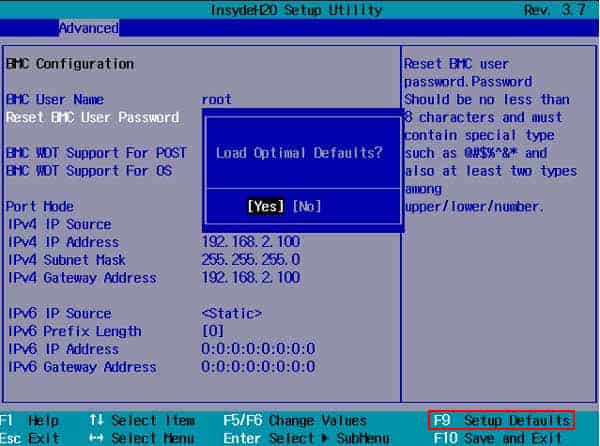
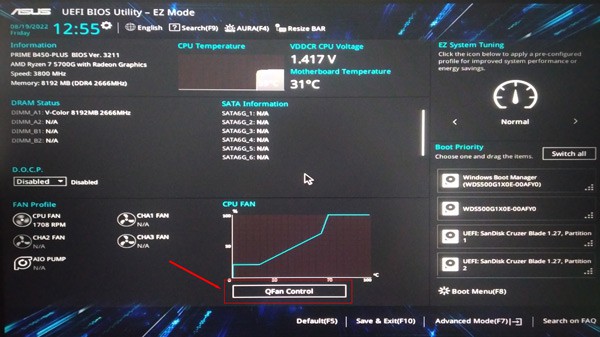
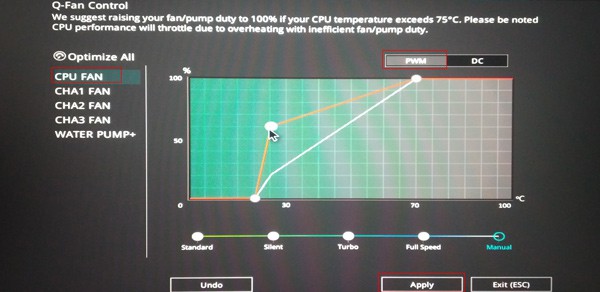
Increase CPU Fan speed
Sometimes the fan speed may not be sufficient to suffice the workload of the processor. This can result in inefficient cooling and eventually overheating of the CPU. However, you can change your CPU fan’s speed if your manufacturer has it unlocked and works in PWM mode. The speed of a DC fan cannot be varied. Let’s see the way to increase fan speed using BIOS. Run your system for a while and see if the CPU crosses its threshold temperature again. If your BIOS does not have the advanced option to modify fan speed, you can use reliable third-party applications such as MSI-Afterburner, SpeedFan, etc.
Delid Your CPU (Only for Professional Users)
If you want to keep your CPU temperature reduced further, then you can perform its delidding. It is the process of removing the top metal portion (lid) of the CPU. The metal portion and the actual circuit consist of minute air pockets that raise the temperature. The metal lid is kept there only for protection. Removing it will bring the CPU in direct contact with the heat sink, improving the cooling efficiency much more. It can even reduce the temperature while keeping the CPU overclocked. The basic process is that you need to remove the lid, scrub the Integrated Heat Spreader (IHS) and apply the new one. But the process is risky and requires a lot of steps. We have provided a detailed guide demonstrating the safe process of delidding the CPU.